When cleaning up vomit, feces, respiratory secretions, or any bodily fluid in the bathroom, classroom, gym or cafeteria it is recommended to wear gloves for protection. Infections such as Staph, Strep, Salmonella, E. Coli, Hepatitis A, TB, and other viruses are transmitted this way.
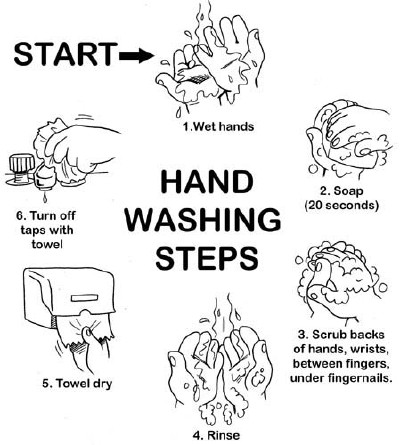 Good Hand Hygiene is the single most effective method of preventing infectious disease. After removing your soiled gloves make sure you wash your hands with soap and water.
Good Hand Hygiene is the single most effective method of preventing infectious disease. After removing your soiled gloves make sure you wash your hands with soap and water.
What if I can't get to gloves, and my hands or clothing become contaminated with blood or bodily fluids? What should I do? Immediately wash hands with an antiseptic or soap and water. Remove soiled clothing as quickly as possible and wash with bleach and water. Notify the School Nurse or School Administrator to see if follow up testing will be necessary.
Each student and employee has the Right to Confidentiality. Each student's diagnoses should be kept confidential. Whether it be a child that has been diagnosed with TB, Hepatitis C, or even head lice we must keep the child's condition confidential.

In Oklahoma less than 6,000 cases of HIV and AIDS were reported in the year 2005, this number is currently higher. In the U.S. in the year 2005, New York had the highest number of reported cases of HIV at 172,377, California followed with 139,019, Florida with 100,809 and then Texas with 67,227. In 2005, approximately 1.2 million cases of HIV were reported. This number is currently higher with 40,000 new cases reported annually.HIV is transmitted through blood to blood contact, (sharing needles, tatooing, IV drug abuse, accidental needle sticks and exposure to contaminated blood), semen, and vaginal secretions (unprotected oral, anal, or vaginal sex), and expectant mother to baby (breast milk).
There are no reported cases from the CDC of any one contracting HIV from sweat, saliva, tears, insect bites, dog bites or just everyday casual contact (hugging, kissing, hand shakes, toilet seats). All are just common misconceptions.
Over a period of time the immune system loses it's ability to fight infection and that's when a person develops AIDS, which eventually leads to death. There is treatment for symptoms, but no cure for HIV.
Transmission of HIV is on the rise, with teenagers being the group that is increasing in numbers the fastest due to unprotected sex and IV drug abuse.
Hepatitis B
Hep. B is transmitted through blood to blood contact, unprotected sex, and expectant mother to baby. This virus is transmitted from person to person more so than HIV. There is no cure for Hepatitis B, only treatment for the symptoms.There is a vaccine for Hep. B. A series of three shots is given over a 6 month period. All children attending school in the state of Oklahoma are required to have their Hep. B vaccination. Adults are encouraged to become vaccinated also, especially if you give first aid treatment often.

